 DocMath-Eval
DocMath-Eval
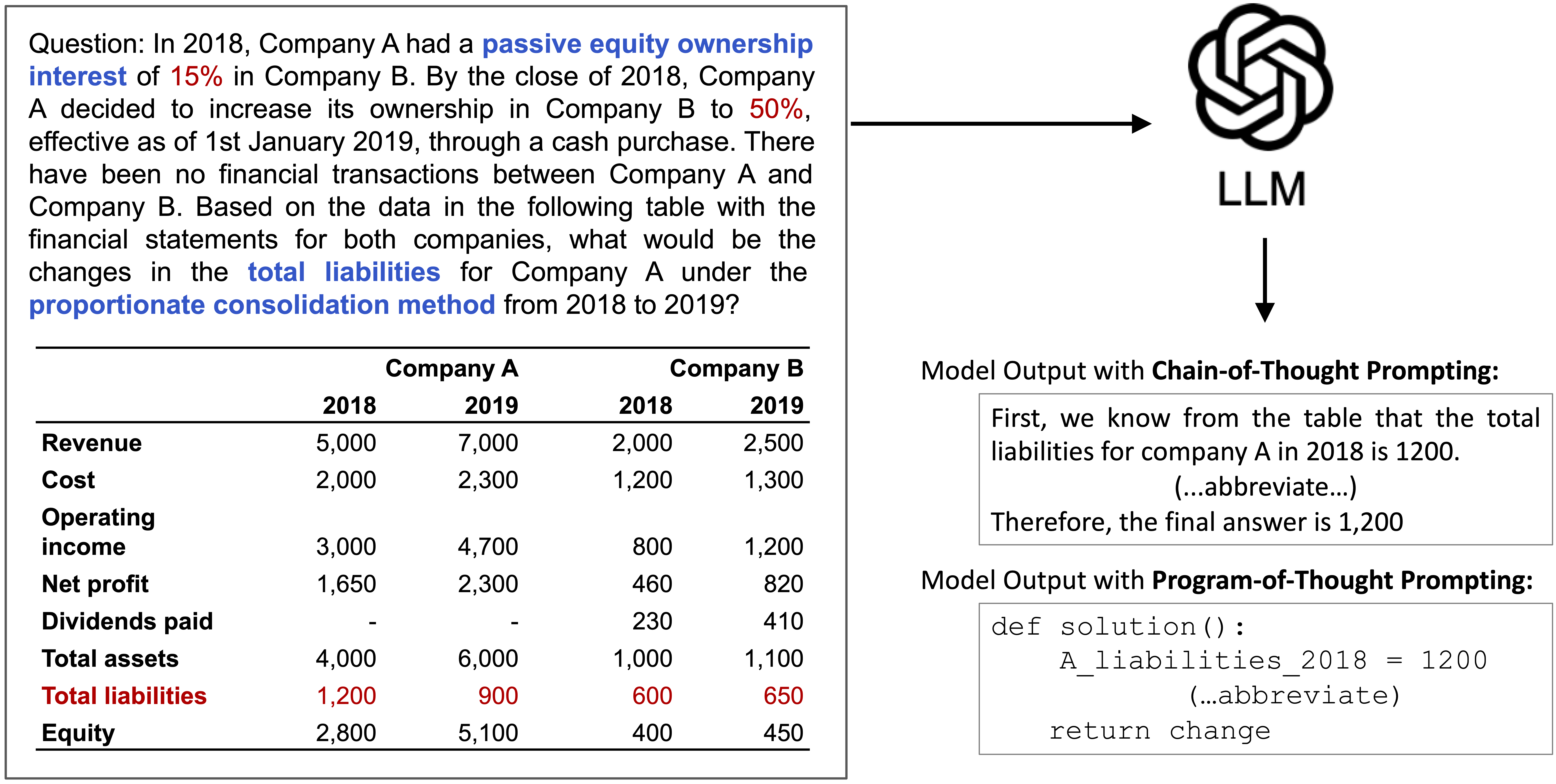
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown impressive capabilities in solving math word problems, but their ability to perform numerical reasoning in specialized domains with complex documents remains understudied. To address this gap, we present DocMath-Eval, a benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs' numerical reasoning skills in interpreting finance-specific documents containing both text and tables. DocMath-Eval consists of four evaluation sets with varying levels of difficulty in numerical reasoning and document understanding:
🚨 To submit your results to the leaderboard, please send to this email with your result json files.
🚨 For more submission details, please refer to this link.
@misc{zhao2024docmatheval,
title={DocMath-Eval: Evaluating Math Reasoning Capabilities of LLMs in Understanding Long and Specialized Documents},
author={Yilun Zhao and Yitao Long and Hongjun Liu and Ryo Kamoi and Linyong Nan and Lyuhao Chen and Yixin Liu and Xiangru Tang and Rui Zhang and Arman Cohan},
year={2024},
eprint={2311.09805},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.09805},
}